调用SpringbootApplication.run()之后到底发生了什么?
1. 观察现象
让我们看一段Spring Boot应用启动日志
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
Spring的启动日志中,总共出现了:
MyInitializer
MyAppAutoConfiguration
DemoListener
EmoListener
GoodListener
AlphaRunner
BetaRunner
GammaRunner
共计8个自定义类,分属四种拓展形式。我们可以看到,它们的输出有特定顺序,并且可以人为调整。接下来,让我们阅读SPringbootApplication.run()方法的源码,了解Springboot是如何启动应用的。
2. 第一步 SpringbootApplication.run()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @SpringBootApplication public class SpringDemoApplication {public static void main (String[] args) {
当我们执行上面这样的代码时,spring完成了两件工作:
创建SpringApplication实例
执行SpringApplication的run方法
2.1. 创建SpringBootApplication实例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) public SpringApplication (ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {this .resourceLoader = resourceLoader;"PrimarySources must not be null" );this .primarySources = new LinkedHashSet <>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));this .webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();this .bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList <>(this .mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
这里创建了一个SpringApplication实例,resourceLoader为null,primarySources是我们的启动类SpringDemoApplication.class。先通过WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath()判断应用类型;然后通过getSpringFactoriesInstances()访问*.factories文件,以类似SPI加载的方式获取服务配置;最终完成SpringApplication实例的初始化工作。
2.2. 执行SpringApplication的run方法
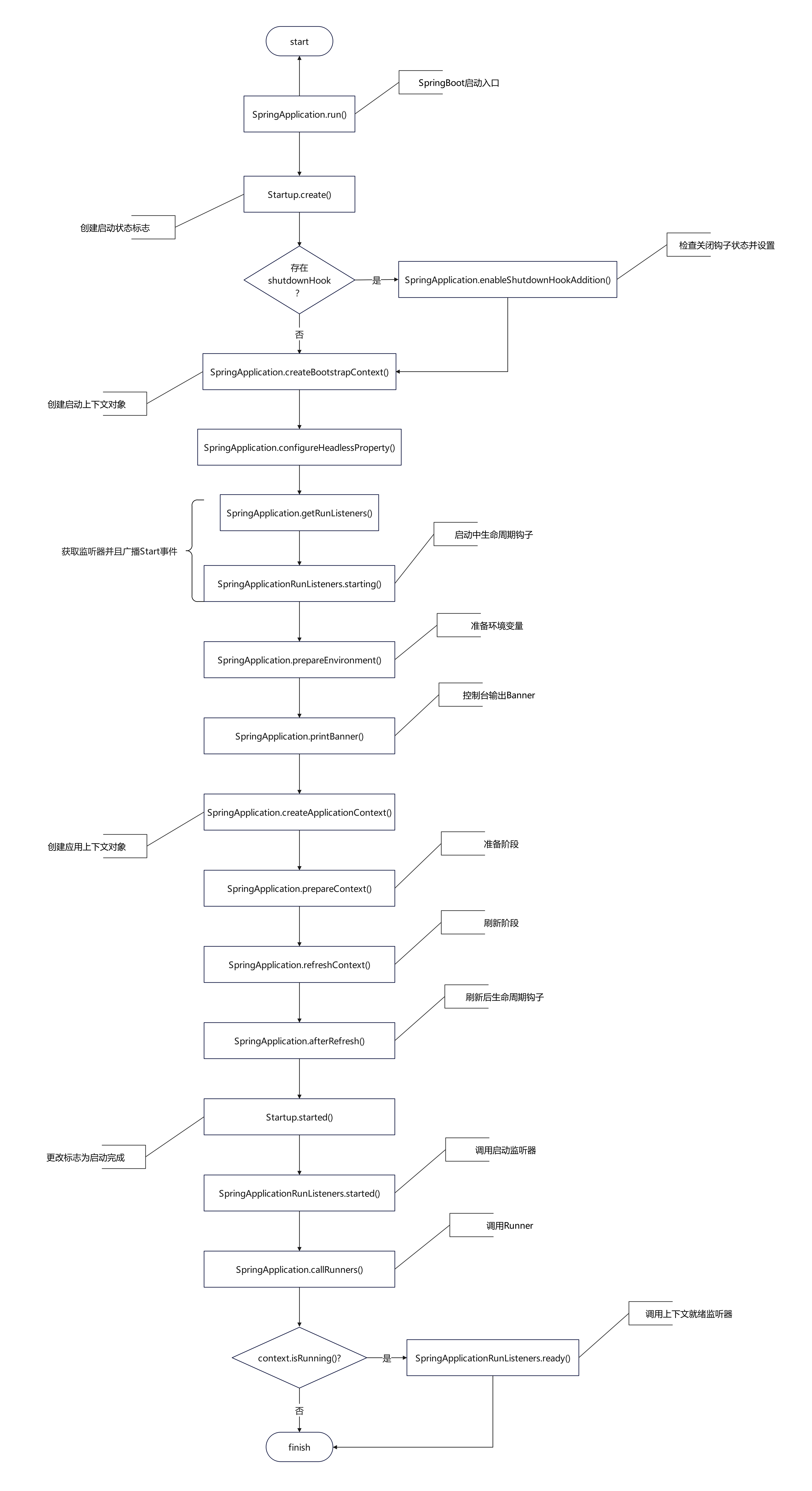
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public ConfigurableApplicationContext run (String... args) {Startup startup = Startup.create();if (this .registerShutdownHook) {DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null ;SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);this .mainApplicationClass);try {ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments (args);ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);this .applicationStartup);if (this .logStartupInfo) {new StartupInfoLogger (this .mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), startup);catch (Throwable ex) {if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {throw ex;throw new IllegalStateException (ex);try {if (context.isRunning()) {catch (Throwable ex) {if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {throw ex;null );throw new IllegalStateException (ex);return context;
run方法的流程可以拆分为以下三个主要阶段:
准备阶段
启动阶段
善后阶段
2.2.1. 准备阶段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Startup startup = Startup.create();if (this .registerShutdownHook) {DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null ;SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);this .mainApplicationClass);
准备阶段按顺序完成以下工作:
调用Startup.create()创建启动标志
如果有注册关闭事件的生命周期钩子,开启对应的生命周期钩子
创建启动上下文
配置无头模式
获取监听器
发布启动事件
其中,下面的日志发生在第三步,创建启动上下文时。
1 2 02:55:58.664 [main] INFO com.example.springdemo.initializer.MyInitializer -- Initializing MyInitializer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext () {DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext ();this .bootstrapRegistryInitializers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.initialize(bootstrapContext));return bootstrapContext;@Slf4j public class MyInitializer implements BootstrapRegistryInitializer {@Override public void initialize (BootstrapRegistry registry) {"Initializing MyInitializer" );
当调用forEach方法挨个执行从spring.factories中读取的BootstrapRegistryInitializer接口的实现类时,便会调用initialize接口,本例中仅输出一条日志。
第5步获取监听器配置是一个重要的拓展模式。请注意SpringApplicationRunListener的定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {default void starting (ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {default void environmentPrepared (ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {default void contextPrepared (ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {default void contextLoaded (ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {default void started (ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {default void ready (ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {default void failed (ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
可以看到,Springboot为上下文设置了七个生命周期状态,即七个拓展点。分别是:
starting——在run方法启动时触发,可以用于执行非常早期的初始化动作。通过run方法的源码可以知道,该钩子在创建好启动上下文(DefaultBootstrapContext)即被调用
environmentPrepared
contextPrepared
contextLoaded
started
ready
failed
我们可以通过实现SpringApplicationRunListener接口并利用spring.factories将实现类植入spring中,用于在正确的生命周期钩子处完成目标工作。作为举例我们可以观察其中一个实现类org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener,正是这个类实现了将上下文钩子事件广播出去的需求。
2.2.2. 启动阶段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments (args);ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);this .applicationStartup);if (this .logStartupInfo) {new StartupInfoLogger (this .mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), startup);
正式的应用上下文(区别于启动上下文)是在上述代码中创建并且配置的。大致步骤如下:
准备环境参数
创建应用上下文
准备应用上下文
刷新应用上下文
调用生命周期函数
调用Runner
2.2.2.1. 准备环境参数
这一步以打印标题为结束标志,即我们常说的Banner。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 . ____ _ __ _ _
ApplicationArguments对象代表了命令行启动时输入的参数
ConfigurableEnvironment对象则表示读取到的环境变量
2.2.2.2. 创建应用上下文
通过调用ApplicationContextFactory的抽象工厂方法,实际通过spring.factories委派至对应的工厂实现创建应用上下文。一般我们在需要创建定制上下文时可以在此处利用spring.factories机制拓展。
本例中,系统委派至ReactiveWebServerApplicationContextFactory实现类。注意,spring的两个web实现,ServletWebServerApplicationContextFactory和ReactiveWebServerApplicationContextFactory都在工厂内实现了aot上下文和非aot上下文的创建。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Override public ConfigurableApplicationContext create (WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {return (webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.REACTIVE) ? null : createContext();private ConfigurableApplicationContext createContext () {if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) {return new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext ();return new ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext ();
2.2.2.3. 准备应用上下文
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 private void prepareContext (DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {this .initializers);if (this .logStartupInfo) {null );ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();"springApplicationArguments" , applicationArguments);if (printedBanner != null ) {"springBootBanner" , printedBanner);if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory autowireCapableBeanFactory) {this .allowCircularReferences);if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory) {this .allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);if (this .lazyInitialization) {new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor ());if (this .keepAlive) {KeepAlive keepAlive = new KeepAlive ();new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor (context));if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) {"Sources must not be empty" );new Object [0 ]));
spring在此处完成上下文的初始化工作,诸如:为上下文设置环境变量,初始化Bean工厂的设定,执行ApplicationContextInitializer对上下文进行自定义初始化,注册启动参数以及Banner的单例,配置循环引用开关,注册懒加载处理器等等
其中,有如下拓展点可用于定制:
通过继承SpringApplication类,重写postProcessApplicationContext方法实现上下文的调整。如默认的SpringApplication类在该方法中完成对beanNameGenerator、resourceLoader、conversionService的初始化设定
实现ApplicationContextInitializer,自定义上下文的初始化。ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类需要写在spring.factories中,以便于Spring在启动时可以将其载入SpringApplication类的initializers属性中。当执行至applyInitializers方法时,便会遍历getInitializers方法返回的列表,逐个调用加载的ApplicationContextInitializer实现类完成自定义初始化。需要注意,getInitializers方法会根据实现类上的Order注解进行排序。
2.2.2.4. 刷新应用上下文
这一步非常重要,前面的步骤中我们仅完成了上下文的创建,基础参数设置和部分初始化工作,我们书写的bean并没有被注册到上下文中。Spring正是通过refresh操作完成所有自定义bean的注册和启动工作。以webflux的启动为例,这里的调用链有些复杂,请看下图说明:
2.2.3. 善后阶段
3. 总结